Interesting Facts for Educators!

If you removed all the empty space in our atoms, the human race, all 6 billion of us on the planet, could fit inside a single sugar cube
The atoms that make up the world around us seem solid but are in fact over 99.99999 per cent empty space. An atom consists of a tiny, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons, spread over a proportionately vast area. This is because as well as being particles, electrons act like waves. Electrons can only exist where the crests and troughs of these waves add up correctly. And instead of existing in one point, each electron’s location is spread over a range of probabilities – an orbital. They thus occupy a huge amount of space.
This astonishing discovery that atoms are mainly empty was made in 1909 at Manchester University by the indefatigable Ernest Rutherford.
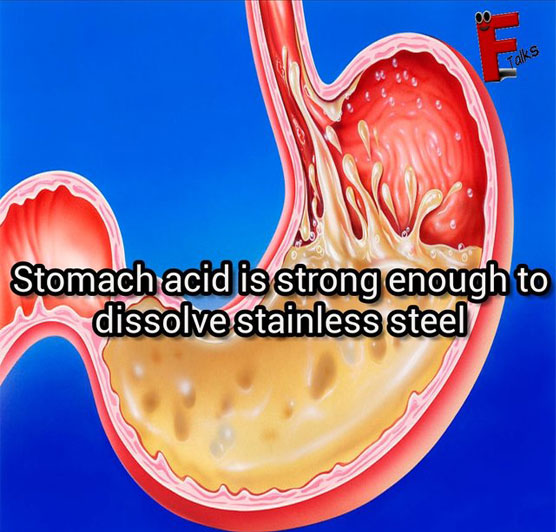
Stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve stainless steel
Your stomach digests food thanks to highly corrosive hydrochloric acid with a pH of 2 to 3. This acid also attacks your stomach lining, which protects itself by secreting an alkali bicarbonate solution. The lining still needs to be replaced continually, and it entirely renews itself every four days.

It takes 8 minutes, 19 seconds for light to travel from the Sun to the Earth
In space, light travels at 300,000 kilometres (186,000 miles) per second. Even at this breakneck speed, covering the 150 million odd kilometres (93 million miles) between us and the Sun takes considerable time. And eight minutes is still very little compared to the five and a half hours it takes for the Sun’s light to reach Pluto.

Some metals are so reactive that they explode on contact with water
There are certain metals – including potassium, sodium, lithium, rubidium and caesium – that are so reactive that they oxidize (or tarnish) instantly when exposed to air. They can even produce explosions when dropped in water! All elements strive to be chemically stable – in other words, to have a full outer electron shell. To achieve this, metals tend to shed electrons. The alkali metals have only one electron on their outer shell, making them ultra-keen to pass on this unwanted passenger to another element via bonding. As a result they form compounds with other elements so readily that they don’t exist independently in nature.
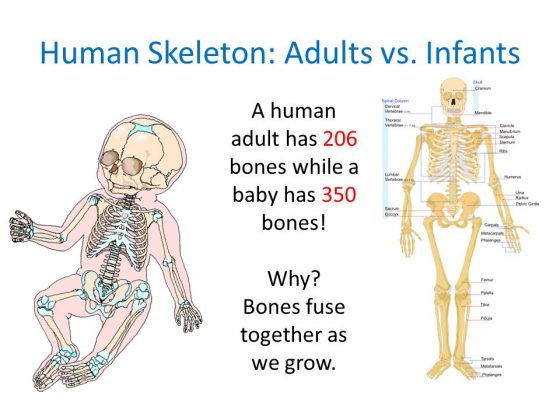
Babies have around 100 more bones than adults
Babies have about 300 bones at birth, with cartilage between many of them. This extra flexibility helps them pass through the birth canal and also allows for rapid growth. With age, many of the bones fuse, leaving 206 bones that make up an average adult skeleton.
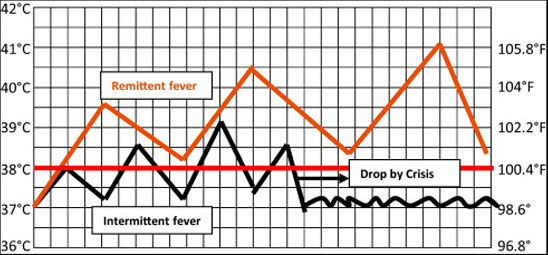
Why does your temperature fluctuate when you have a fever?
When you have an infection, your body produces white blood cells to fight it. These affect your hypothalamus, the area of your brain that controls body temperature, causing you to heat up. In response your blood vessels tighten, causing your outer layer of skin to cool and your muscles to contract, making you shiver. Shivering produces more heat, raising your temperature again.
Later, the amount of heat you lose and make levels out and your body stays at a high temperature. When you’ve fought off the infection, your blood vessels open up and you sweat, cooling you down again.
